Did you know that we spend nearly one-third of our lives asleep? That equals about 26 years of an average lifespan! Yet, despite the massive role sleep plays in our health, very few of us consider the way we position our bodies at night. According to surveys by the National Sleep Foundation, more than 60% of adults sleep in positions that may actually hurt their long-term health instead of helping it.
Here’s the surprising truth: not all sleep positions are created equal. Some are neutral, some beneficial, and one in particular is considered the most dangerous for your spine, breathing, and overall recovery. In this article, we’ll explore which sleep position could be silently affecting your health, why it matters more than you think, and the proven steps you can take tonight to instantly improve your rest.
By the end, you’ll understand how a simple shift in your nightly routine could boost energy, reduce pain, and even improve your heart health. Ready to find out if you’re making the mistake millions of people do every single night? Let’s dive in.
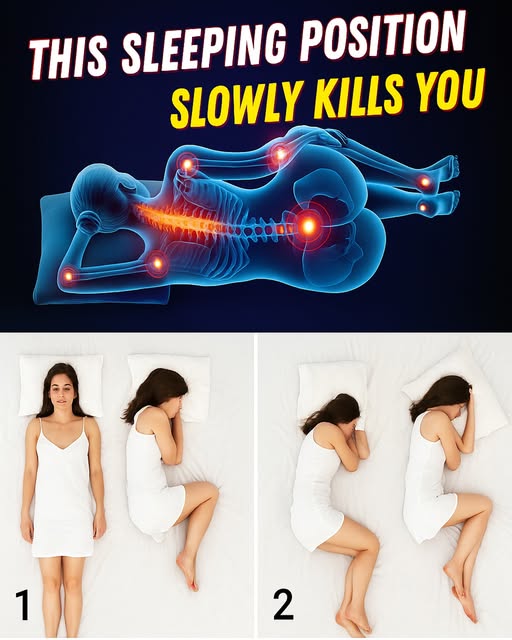
Why Sleep Position Matters More Than You Realize
Most people assume that as long as they get 7–8 hours of sleep, they’re doing fine. But the way your body is aligned during those hours can either help your body recover, repair, and rejuvenate—or create silent strain that builds up over years.
The Science of Sleep Alignment
When you sleep, your muscles relax, your heart rate lowers, and your breathing slows. Ideally, your body should remain in a position that keeps the spine neutral, lungs open, and blood circulating without restriction. However, certain positions cause:
- Restricted airway flow → leading to snoring or sleep apnea.
- Spinal misalignment → resulting in morning stiffness or chronic pain.
- Poor circulation → linked to numbness, tingling, or even cardiovascular strain.
- Slower muscle recovery → making you feel drained even after “a full night’s sleep.”
Think of your sleep position like the foundation of a house. If the foundation is misaligned, the structure eventually cracks.
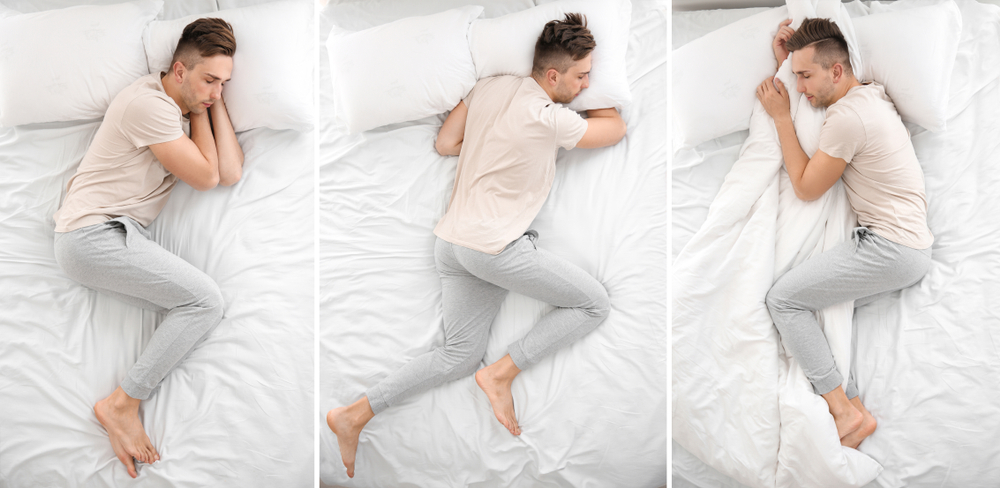

The Most Dangerous Sleep Position Revealed
So, what’s the worst sleep position you can be in?
It’s sleeping on your stomach.
Why Sleeping on Your Stomach is Harmful
At first glance, it may feel comfortable—many people with insomnia actually find it easier to fall asleep this way. But here’s what science says happens when you spend hours in this position:
- Neck Strain
Your head must turn to one side to breathe, twisting your neck unnaturally. Over time, this leads to chronic neck pain, pinched nerves, and tension headaches. - Spinal Misalignment
Sleeping face-down flattens the natural curve of your spine. This compresses discs and puts stress on the lower back, increasing the risk of long-term back pain. - Restricted Breathing
With your chest pressed into the mattress, your lungs have less room to expand. This makes breathing shallower and can worsen snoring or sleep apnea. - Increased Pressure on Joints
The unnatural angle of the shoulders and hips can cause numbness, tingling, and even joint inflammation.

Case Study Example
A 38-year-old office worker reported daily lower back pain despite regular exercise. After a sleep clinic evaluation, the culprit wasn’t his chair or gym form—it was his stomach sleeping habit. Switching to side sleeping with a pillow between his knees reduced his pain by 70% within one month.
Healthier Alternatives: The Best Sleep Positions
If stomach sleeping is the most dangerous, what should you do instead? Experts highlight two main positions that support long-term health.
1. Sleeping on Your Back
This is often considered the healthiest sleep position because it evenly distributes body weight and keeps the spine aligned.
Benefits:
- Reduces pressure on joints.
- Supports head, neck, and spine alignment.
- May minimize acid reflux when slightly elevated.
Tips:
- Use a supportive pillow under your head and a smaller one under your knees.
- Avoid overly thick pillows that tilt the neck forward.

2. Sleeping on Your Side
Side sleeping is especially popular and comes with powerful benefits, especially for people with sleep apnea or acid reflux.
Benefits:
- Keeps airways open, reducing snoring and breathing issues.
- Supports digestion and reduces acid reflux.
- Improves circulation during pregnancy.
Tips:
- Place a pillow between your knees to align hips and spine.
- Switch sides occasionally to avoid shoulder stiffness.

Comparison Table
| Sleep Position | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stomach | May feel comforting at first | Neck strain, spinal misalignment, breathing issues | Not recommended |
| Back | Spine alignment, joint relief, less wrinkling | May worsen snoring or sleep apnea | Healthy adults without breathing issues |
| Side | Airway support, digestion aid, circulation | Possible shoulder/hip strain | People with snoring, reflux, pregnancy |
How to Break the Stomach-Sleeping Habit
Changing your sleep position isn’t easy—it’s a deeply ingrained habit. But with patience and consistency, you can retrain your body.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Start with Pillow Placement
Place a firm pillow under your knees if sleeping on your back, or between your knees if sleeping on your side. This discourages rolling forward. - Use a Body Pillow
Hugging a long pillow mimics the comfort of stomach sleeping while keeping you aligned. - Gradually Adjust
Begin with short naps in your new position, then progress to full nights. - Invest in the Right Mattress
Medium-firm mattresses are ideal for side or back sleeping. Too soft encourages stomach sinking. - Mindset Shift
Remind yourself: every night you avoid stomach sleeping, you’re preventing years of pain and discomfort down the road.

Everyday Life Benefits of Better Sleep Position
When you finally commit to a healthier sleep posture, the improvements extend far beyond mornings.
- More Energy: Proper breathing during sleep improves oxygen flow, helping you wake refreshed.
- Better Posture: Correct spinal support at night encourages better posture during the day.
- Pain Relief: Chronic back and neck pain often decreases dramatically.
- Sharper Focus: Quality sleep means better memory and concentration.
- Mood Balance: Poor sleep is linked to irritability, while good sleep supports emotional resilience.
A simple change in the way you position your body could literally transform how you feel every day.
Conclusion
Is stomach sleeping dangerous? Yes, it’s the worst position for your health.
Which position is best? Back sleeping for overall alignment, side sleeping for airway and digestion support.
Can you change your habit? Absolutely—with the right pillows, mattress, and mindset.
What’s the first step tonight? Try using a pillow to support your new position and see how your body feels in the morning.
Remember, small nightly changes can create lifelong benefits.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. If you have chronic sleep issues, consult with a qualified healthcare provider for personalized guidance.




