Did you know that nearly one-third of your life is spent in bed? Sleep is not just about getting enough hours—it’s also about how and where you sleep. Surprisingly, research and traditional wellness practices suggest that choosing the left side of the bed may impact your health in profound ways. From better digestion to improved heart function, small adjustments in your sleep position and side of the bed can make a noticeable difference.
Imagine this: two people sleep the same number of hours, yet one wakes up energized while the other feels sluggish. Could something as simple as the side of the bed be influencing this? In this article, we’ll explore why sleeping on the left side of the bed has been linked to unique health benefits. You’ll learn practical insights from science, traditional medicine, and real-life experiences that might just change the way you think about bedtime forever.
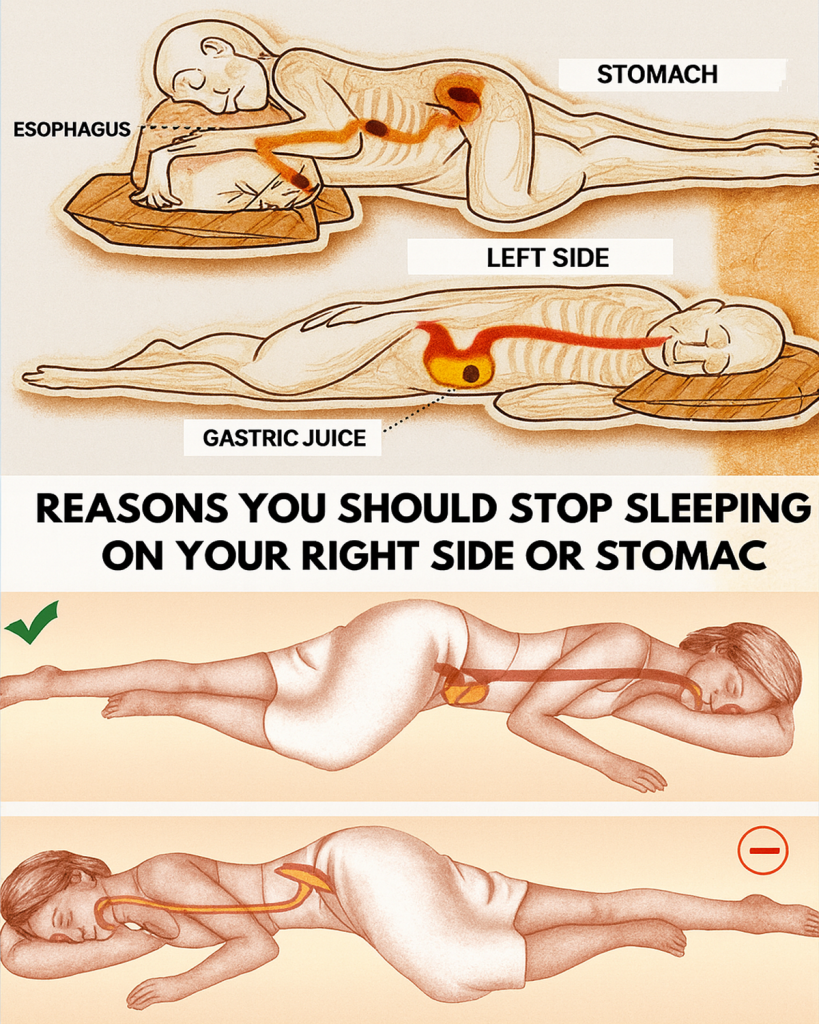
The Science Behind Sleep Positions
While sleep researchers often focus on duration and quality, body position is just as crucial. Gravity, organ placement, and circulation all play roles in how efficiently your body restores itself overnight. Sleeping on the left side may:
- Encourage smoother digestion because the stomach naturally curves leftward.
- Improve lymphatic drainage, helping your body clear toxins.
- Support better circulation, especially for people with certain heart conditions.
These physiological reasons explain why both ancient Ayurvedic practices and modern medical observations emphasize the left-side preference.
1. Digestive Benefits of the Left Side
Your stomach and pancreas naturally sit on the left side of the body. Sleeping in this position encourages food waste to move more easily into the intestines.

Everyday Example: People who suffer from acid reflux often find relief by lying on their left side. A small lifestyle shift like this can minimize nighttime discomfort and reduce the need for over-the-counter medications.
Quick Tip: If you tend to snack late, lying on the left side after meals may ease bloating and promote smoother digestion.
2. Heart Health and Circulation
For the heart, the left side of the bed aligns with how blood flows through your body. Sleeping on the left can reduce pressure on the heart muscle, making circulation easier.
Case Study: Pregnant women are often advised to sleep on their left side because it promotes better blood flow to the placenta, ensuring oxygen supply to the baby. This same principle applies to everyday heart function for adults.
Pro Insight: People with high blood pressure sometimes report that sleeping on the left helps them feel calmer upon waking.

3. Supporting the Lymphatic System
Your lymphatic system is like the body’s natural sanitation service, filtering waste and supporting immunity. Because lymphatic drainage tends to be more efficient on the left side, this position may give your body a head start on detoxifying overnight.
Everyday Note: If you wake up feeling groggy despite sleeping enough hours, it could be that your body isn’t clearing toxins as efficiently. Trying the left-side position may help.
4. Relieving Varicose Veins and Leg Pain
Varicose veins and swelling in the legs can worsen if circulation is sluggish. Sleeping on the left side reduces pressure on the vena cava—the large vein that carries blood from the legs back to the heart.
Example: Older adults or people with sedentary jobs have noticed reduced morning swelling in their ankles after adopting left-side sleeping.
Tip: Elevating the legs slightly with a pillow while on the left side enhances circulation further.

5. Brain Health and Sleep Quality
During deep sleep, your brain undergoes a “cleaning” process, flushing out waste proteins linked to cognitive decline. Some studies suggest that side sleeping—especially on the left—may support this natural detox pathway more effectively than back or stomach positions.
Everyday Insight: People who report restless nights sometimes find more restful sleep after consciously switching to the left side of the bed.
6. Emotional and Psychological Benefits
Interestingly, the side of the bed can also influence mood and emotional health. Surveys have found that people who sleep on the left side often report waking up in a better mood compared to right-side sleepers. While this could be psychological, the physical benefits like better digestion and circulation likely contribute.
Lifestyle Example: Couples sometimes find that swapping sides of the bed changes morning energy levels. One partner may feel more refreshed when moving to the left.

Practical Tips for Making the Switch
- Start gradually: If you’re used to the right side, try switching for a few nights a week.
- Use pillows: Place one behind your back to prevent rolling over during the night.
- Optimize the environment: Ensure your mattress supports side sleeping to avoid shoulder or hip discomfort.
- Consistency matters: Benefits often become noticeable after a few weeks of consistent left-side sleeping.
Quick Reference Table
| Health Concern | Why Left Side Helps |
|---|---|
| Acid Reflux | Reduces stomach acid flow back into the esophagus |
| Heart Health | Less pressure on heart, better circulation |
| Pregnancy | Improves blood flow to placenta |
| Varicose Veins | Relieves pressure on vena cava |
| Brain Detox | Supports natural waste-clearing during deep sleep |
Conclusion
Sleeping on the left side of the bed may seem like a small lifestyle choice, but it can deliver big benefits for digestion, circulation, and overall well-being. From easing acid reflux to supporting the heart and lymphatic system, this position aligns with both traditional wisdom and modern medical insights.
In Summary
- Left-side sleeping improves digestion and heart health.
- It supports circulation, lymphatic function, and brain detox.
- People often wake up feeling lighter, calmer, and more refreshed.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your sleep habits.




