Did you know that bedbugs have been found in nearly every country across the globe, with the United States experiencing a sharp rise in infestations over the past two decades? According to surveys, one out of five Americans has either dealt with bedbugs personally or knows someone who has. This tiny insect, only about the size of an apple seed, has been tormenting humans for centuries. But here’s the unsettling truth: bedbugs don’t just invade dirty homes—they can live anywhere, from luxury hotels to spotless apartments.
This article dives deep into how bedbugs live, why they are so difficult to control, and the most effective strategies to eradicate them from your home. You’ll learn where they hide, how to spot early signs, the dangers they pose, and both natural and professional solutions to get rid of them for good. By the end, you’ll be armed with knowledge and actionable steps to protect your home and family from one of the most persistent pests known to mankind.
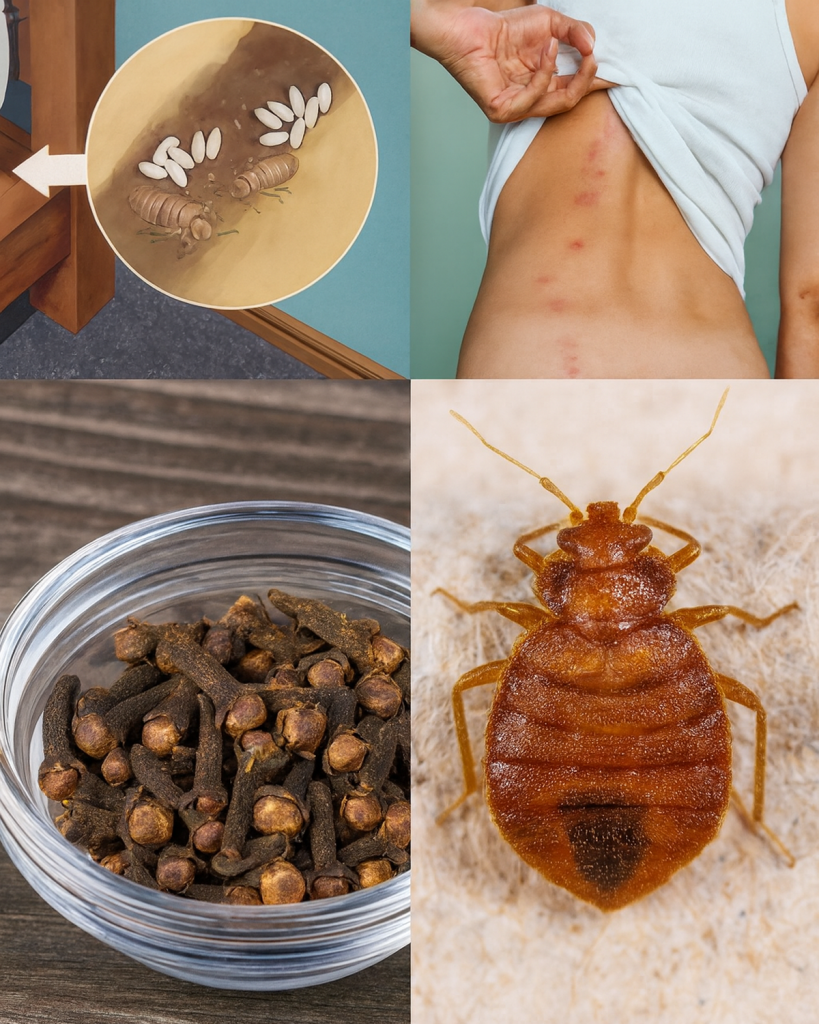

Understanding Bedbugs: Life Cycle and Habits
Bedbugs (Cimex lectularius) are parasitic insects that feed exclusively on blood. Humans are their preferred hosts, though they can also bite animals. To effectively eliminate them, you must first understand their biology.
Life Cycle of Bedbugs
Bedbugs pass through five nymph stages before reaching adulthood. Each stage requires at least one blood meal to develop further.
| Stage | Appearance | Duration (approx.) | Feeding Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg | White, pinhead-sized | 6–10 days | None |
| Nymph 1 | Translucent, tiny | 5–7 days | 1 blood meal |
| Nymph 2–4 | Gradually darker | 1–2 weeks each | 1 blood meal per stage |
| Adult | Brown, 5–7 mm | Up to 12 months | Weekly blood meals |
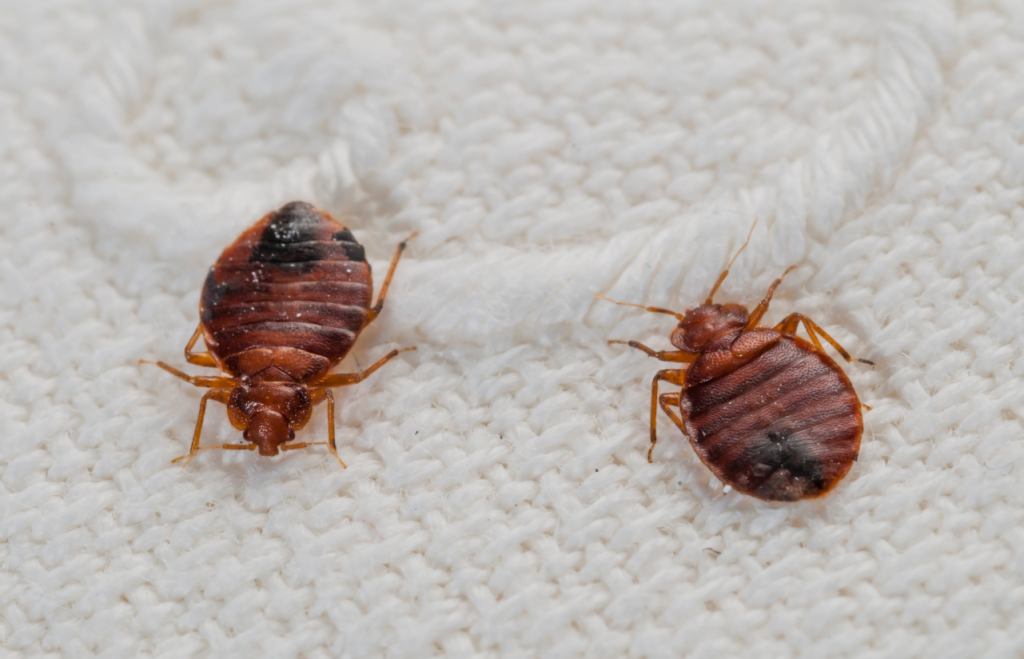

Behavior and Habits
- Feeding Time: Bedbugs are nocturnal, feeding mostly at night while their host is asleep.
- Feeding Method: They pierce the skin with two hollow tubes—one injects saliva with anticoagulants and anesthetics, the other draws blood.
- Hiding Places: They squeeze into cracks, mattress seams, furniture joints, electrical outlets, or behind wallpaper.
- Survival Ability: Bedbugs can survive months without feeding, making them hard to starve out.
Understanding these habits explains why infestations spread so quickly and why eradication requires persistence.
How to Identify a Bedbug Infestation
Bedbug infestations are often confused with flea bites or allergic reactions. Correct identification is crucial.
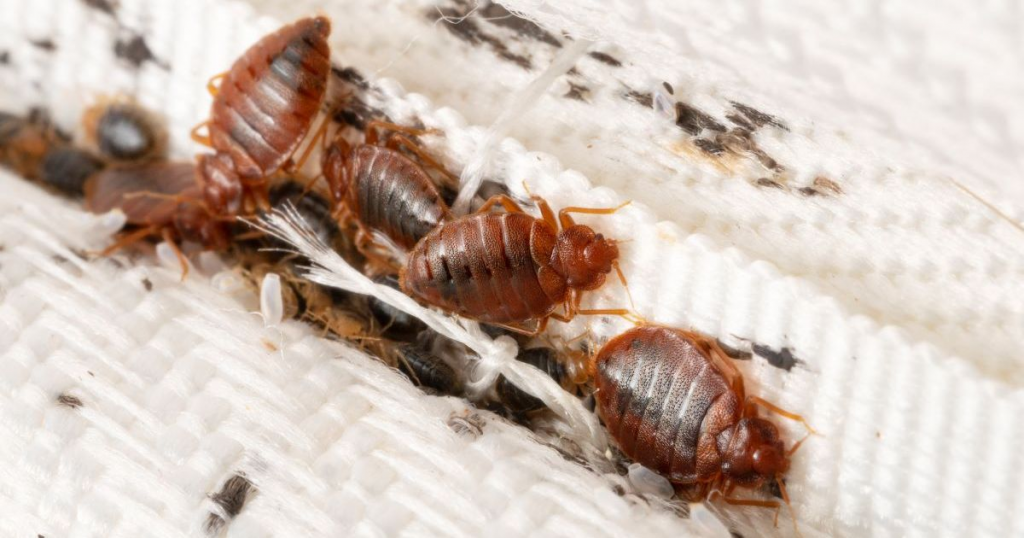

Signs of Bedbug Presence
- Bites on Skin: Red, itchy welts, often in clusters or lines, usually on arms, legs, or exposed skin during sleep.
- Stains on Bedding: Small rust-colored or dark spots, caused by crushed bedbugs or excrement.
- Musty Odor: A sweet, unpleasant smell from large infestations.
- Shed Skins: Exoskeletons left behind as they grow.
- Live Bugs: Visible in mattress seams, bed frames, or upholstered furniture.
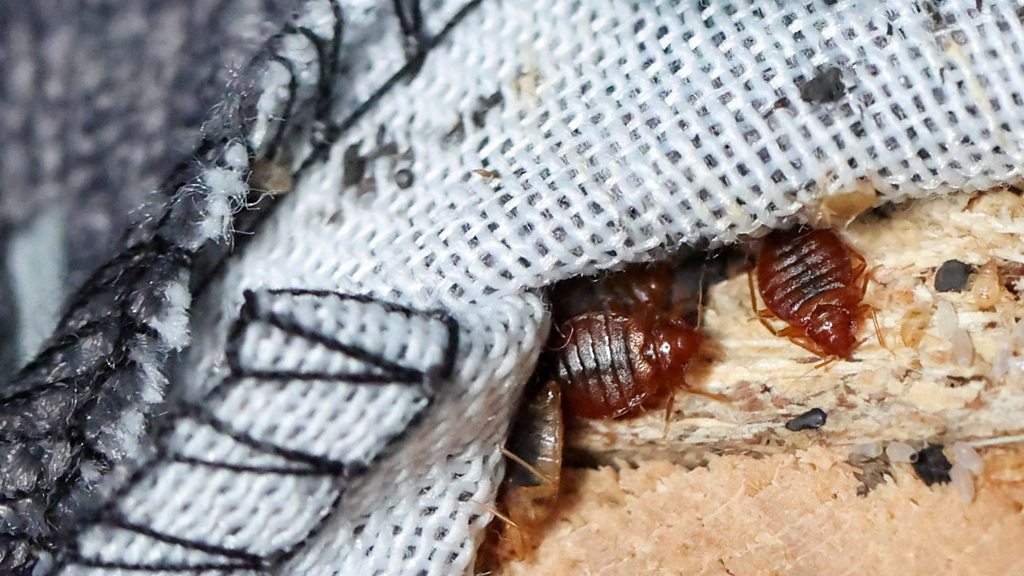
Common Hiding Spots
- Inside mattress seams and box springs
- Cracks in bed frames and headboards
- Behind loose wallpaper or picture frames
- Electrical outlets and baseboards
- Upholstered furniture seams
Regular inspection of these spots is essential if you suspect bedbugs.

Health Risks Associated with Bedbugs
While bedbugs are not known to transmit diseases directly, they pose other health risks.
- Allergic Reactions: Some people experience severe allergic responses to bedbug bites.
- Secondary Infections: Scratching bites may lead to skin infections such as impetigo or cellulitis.
- Sleep Disruption: Anxiety and itching can cause insomnia.
- Mental Health Impact: Prolonged infestations lead to stress, embarrassment, and even depression.
Although they are not lethal, the physical and psychological toll of bedbugs should not be underestimated.
Methods to Eliminate Bedbugs
Getting rid of bedbugs requires a systematic approach. Relying on one method alone is rarely effective.
Step 1: Clean and Declutter
- Wash bedding, clothing, and curtains in hot water (at least 120°F).
- Dry items on high heat for at least 30 minutes.
- Vacuum thoroughly—especially mattress seams, carpets, and crevices.
- Use a stiff brush to dislodge eggs before vacuuming.
Step 2: Encase and Isolate
- Encase mattresses and box springs in special bedbug-proof covers.
- Move beds away from walls and furniture.
- Place bed legs in interceptor traps to prevent climbing.
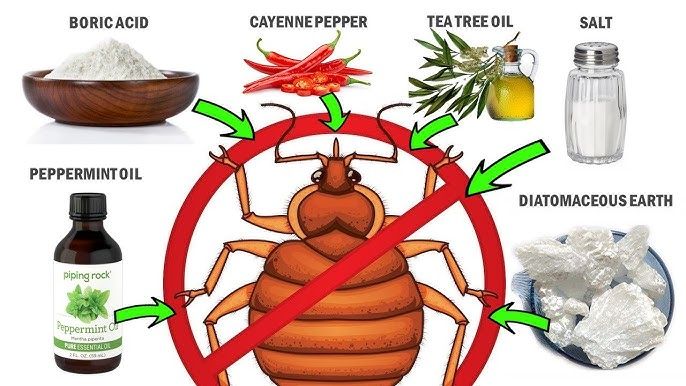
Step 3: Natural Remedies
- Heat Treatment: Expose infested items to direct sunlight or use a dryer. Bedbugs die at temperatures above 118°F.
- Diatomaceous Earth: A natural powder that damages the exoskeleton of bedbugs, leading to dehydration.
- Essential Oils: Oils like tea tree, lavender, and peppermint may repel bedbugs, though they are less effective against heavy infestations.
Step 4: Chemical Treatments
- Over-the-counter sprays with pyrethrins or pyrethroids.
- Use cautiously, as bedbugs have developed resistance in some regions.
- Always follow product instructions to minimize health risks.
Step 5: Professional Extermination
For large infestations, professional pest control is often the only solution. Experts use methods such as whole-room heat treatments, fumigation, or targeted insecticides.

Preventing Future Infestations
Prevention is more cost-effective and less stressful than eradication.
- Inspect hotel rooms when traveling.
- Keep luggage on racks, away from beds and walls.
- Wash travel clothes immediately upon returning home.
- Seal cracks and crevices in your home.
- Vacuum frequently to catch stragglers before they reproduce.
Conclusion
Bedbugs are resilient, stealthy pests that can turn even the cleanest home into a stressful environment. By understanding how they live, spotting early signs, and applying a combination of cleaning, natural remedies, and professional intervention, you can reclaim your home.
FAQ Accordion Style
Q: Can bedbugs live in clean houses?
A: Yes. Cleanliness does not prevent bedbugs since they only need blood to survive.
Q: Do bedbug bites spread diseases?
A: No evidence confirms that bedbugs spread diseases, though they cause allergic reactions and infections from scratching.
Q: What is the fastest way to get rid of them?
A: Professional heat treatment is the most effective and immediate solution.
Q: Are natural remedies enough?
A: They may help in mild cases, but heavy infestations often require professional treatment.
Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical or pest control advice.




